
No liability is assumed with respect to the use of the information contained herein. Transmitted by any means, without prior written permission from the publisher.

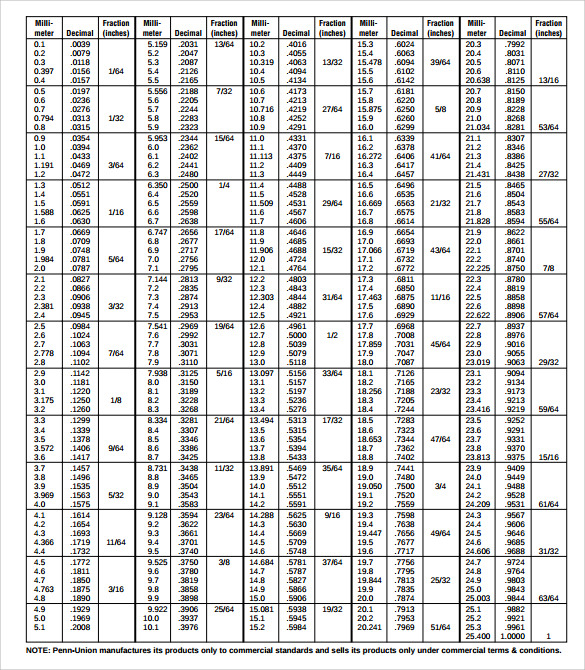
No part of these pages shall be reproduced, stored or Please Visit Our Advertisers!ĬOPYRIGHT © 2004 BY SCIENCE MADE SIMPLE, INC.Īll rights reserved. Note: decimals marked with * are NOT EXACTĪnd have been rounded to 6 decimal places Each decimal fraction has exactly two infinite decimal expansions, one containing only 0s after some place, which is obtained by the above definition of n, and the other containing only 9s after some place, which is obtained by defining n as the greatest number that is less than x, having exactly n digits after the decimal mark.Fraction to decimal conversions chart - fractions and decimals fraction to decimal conversions chart by In summary, every real number that is not a decimal fraction has a unique infinite decimal expansion. either a (finite) sequence of digits (such as "2017"), where the entire sequence represents an integer:Ī m a m − 1 … a 0 is the decimal fraction obtained by replacing the last digit that is not a 9, i.e.: d N, by d N + 1, and replacing all subsequent 9s by 0s (see 0.999.).Īny such decimal fraction, i.e.: d n = 0 for n > N, may be converted to its equivalent infinite decimal expansion by replacing d N by d N − 1 and replacing all subsequent 0s by 9s (see 0.999.).įor representing a non-negative number, a decimal numeral consists of " in many countries (mostly English-speaking), and a comma " ," in other countries. The decimal digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 the decimal separator is the dot ". This system has been extended to represent some non-integer numbers, called decimal fractions or decimal numbers, for forming the decimal numeral system.įor writing numbers, the decimal system uses ten decimal digits, a decimal mark, and, for negative numbers, a minus sign "−". These difficulties were completely solved with the introduction of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system for representing integers. Very large numbers were difficult to represent in these old numeral systems, and only the best mathematicians were able to multiply or divide large numbers. Examples are firstly the Egyptian numerals, then the Brahmi numerals, Greek numerals, Hebrew numerals, Roman numerals, and Chinese numerals. Many numeral systems of ancient civilizations use ten and its powers for representing numbers, possibly because there are ten fingers on two hands and people started counting by using their fingers. Ten digits on two hands, the possible origin of decimal counting ( May 2022) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. An infinite decimal represents a rational number, the quotient of two integers, if and only if it is a repeating decimal or has a finite number of non-zero digits. A repeating decimal is an infinite decimal that, after some place, repeats indefinitely the same sequence of digits (e.g., 5.123144144144144. In this context, the decimal numerals with a finite number of non-zero digits after the decimal separator are sometimes called terminating decimals. The decimal system has been extended to infinite decimals for representing any real number, by using an infinite sequence of digits after the decimal separator (see decimal representation). That is, fractions of the form a/10 n, where a is an integer, and n is a non-negative integer. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. Decimal may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " 3.14 is the approximation of π to two decimals". Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in 25.9703 or 3,1415). Ī decimal numeral (also often just decimal or, less correctly, decimal number), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as decimal notation. It is the extension to non-integer numbers ( decimal fractions) of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary / ˈ d iː n ər i/ or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. For other uses, see Decimal (disambiguation).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
