
Preterite Conjugations: Regular Verbs The pretrito ( preterite) tense is one of the tenses used in Spanish to talk about the past. It’s one of the two used in Spanish to talk about the past. Fui al supermercado clearly means "I went to the supermarket," not *"I was to the supermarket. Quick Answer The pretrito ( preterite) tense is used in Spanish to talk about actions that were completed in the past.Verb) which is usually conjugated in the ImperfectĬonversation will let you know which is being used. This preterite conjugation form will nearly always be Ir (an action verb) rather than Ser (a descriptive
#Do spanish irregular past tense verbs have accents how to
Since Ser refers to existence and identification, it is nearly impossible to use this in the Preterite which handles only completed actions. Caer: Preterite Tense Using the chart below you can learn how to conjugate the Spanish verb caer in Preterite tense. This is not as confusing as it may appear. Remember that Spanish only uses accent marks when required for pronunciation or differentiation. Note: Try to use the correct written accents if you can e.g.: á, é, í, ó, ú, ñ, ü. Such as Dar, Ser, Ir and Ver, also do not wear accent marks in the Preterite. Complete the following sentences with the Preterite of the irregular verbs given in brackets. The -Er/-Ir preterite verb endings rather than - Ar verb endings. Often humorously referred to as the "cross-dressing" verb, because in Verbs which are irregular in the Preterite

Notice that none of these conjugation endings have accent marks! With grossly irregular changes in the Preterite follow this conjugation: Verbs which have an Irregular Preterite form have their own conjugation - differentįrom the established -Ar, -Er/-Ir Preterite conjugation

To regular stem-changing verbs which affect certain -Ir conjugations in the Preterite. (like the verbs ending in -Car, -Gar and -Zar) nor are the changes in vowels similar
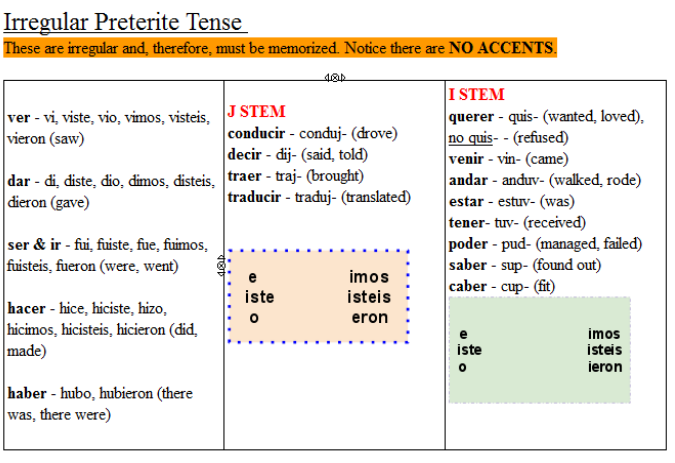
These Irregular preterite changes are NOT for orthographic (spelling) reasons Occur in all of the conjugations (including the nosotros form.) These Irregularįorms in the Preterite are said to have "radical" changes, that is, vowel andĬonsonant changes in the root (or stem of the verb.) Furthermore, these changes If you’re tired of grammar, then take a look at our section on Spanish phrases, with video and audio of native speakers from Spain and Latin America.Number of verbs with irregular conjugation forms in the Preterite. In our Spanish grammar section you’ll find all of the most common (and most useful!) Spanish tenses. The following verbs also have irregular past participles, but follow no set pattern: Verb simple past tense: Subject, Verb, Object. Reírse -> me he reído, te has reído, se ha reído, nos hemos reído, os habéis reído, se han reído Irregular verbs 2 If the sentence did not have either the subject or the main verb, it would not make sense. * You will also hear the participle ‘creído’ used a lot with the meaning of ‘vain’ĭid you notice how reflexive verbs form the Pretérito perfecto compuesto?: conducir to drive, conduje, condujiste dar to give, di, diste decir to say, dije, dijiste estar to be, estuve, estuviste hacer to do, to make, hice, hiciste. Let’s look at examples using this first group of irregular verbs: However, this does not apply to verbs which end in – uir. When – er and – ir verb stems end in a vowel, then the past participles require the addition of an accent. However, not all verbs have a regular past participle. Incorrect: Comedo Irregular verbs 1 – accented past participlesĪll verbs form the Pretérito perfecto compuesto with the auxiliary verb ‘haber’ and the past participle.
Just remember that the past participle for ER verbs uses an ‘I’ instead of an ‘E’: Person /Verbįorming the past participles of regular Spanish verbs is easy: Conjugation for regular verbsĪs you’ll see below, the Pretérito perfecto compuesto is formed by the present tense (present indicative) of the verb haber and the past participle of the verb in question. In this case, the accent you’ll hear is from Madrid, Spain. We have included audio files with this lesson. How to form the Pretérito perfecto compuesto in Spanish. This tense is one of the most common in Spanish and corresponds to the English Present Perfect.Īlongside the Present tense ( presente de indicativo), this is one of the first Spanish tenses that you will need to get to grips with.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
